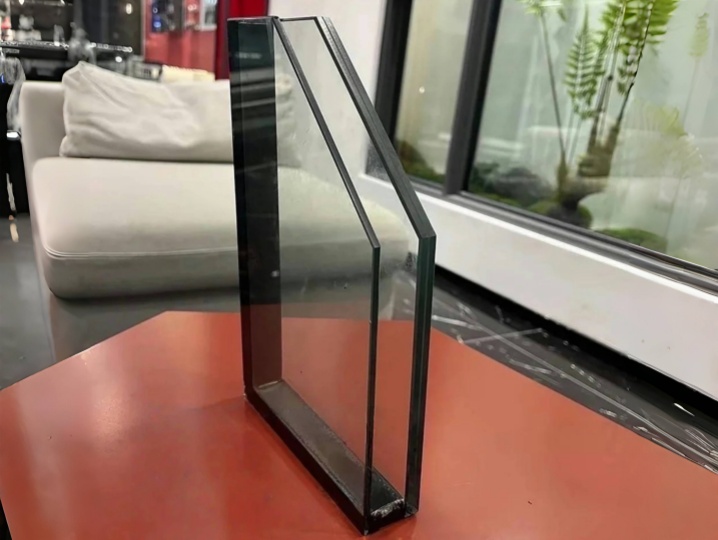
Glass Structure
Laminated glass (8mm + 0.76mm PVB + 8mm) + 16mm Argon + laminated glass (6mm + 0.76mm PVB + 6mm)
Features
Mid- and low-frequency reduction:
The acoustic PVB interlayer absorbs vibration energy, cutting low-frequency noise—such as engines and outdoor AC units—by approximately 8–10 dB.
High-frequency blocking
The argon-filled cavity reduces resonance transmission and blocks high-frequency noise—including voices and amplified music—by around 5–7 dB.
Full-spectrum attenuation
Field-tested overall sound insulation typically reaches 46–49 dB, far outperforming standard IGUs, which usually deliver only 25–30 dB.
Shatter-safe and impact resistant
The PVB interlayer holds glass fragments in place upon breakage, reducing the risk of falling debris and meeting safety glazing requirements.
Improved wind-load performance
Dual laminated layers offer enhanced structural rigidity, ideal for coastal regions, cyclone-exposed areas, and high-rise applications.
Thermal insulation
Argon gas—with its low thermal conductivity—reduces heat transfer through the IGU. This improves summer heat-gain performance by up to 30%, and enhances winter heat retention.
UV protection
The PVB interlayer blocks up to 99% of UV radiation, helping protect interior furnishings from fading.
Applications
Residential:
Street-facing homes or properties near major roads, flyovers and airports where low-frequency noise is significant.
Commercial:
Spaces requiring elevated acoustic performance, such as offices, meeting rooms, studios and recording facilities.
Special Use:
Sunrooms requiring both safety and acoustic control, as well as hospitals, schools and other environments with stringent safety and noise requirements.